

Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is one of the most dynamic and liquid markets in the world. Forex trading involves buying and selling currencies in pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD, to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. Whether you’re new to trading or looking to enhance your understanding, mastering the basics of the Forex market is the first step toward becoming a successful trader. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential concepts of Forex trading, including how it works, key terminology, and the factors influencing currency values. With this foundational knowledge, you’ll be ready to dive deeper into more advanced Forex trading strategies.

Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD, in a decentralized global market. In this section, we will cover the fundamentals of Forex trading to help you understand its core principles and how it works.
Forex trading is the act of exchanging one currency for another in order to profit from changes in exchange rates.
The market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, making it highly liquid and accessible to traders worldwide.
Trading occurs in currency pairs, like USD/JPY, where one currency is bought, and the other is sold.
It’s a decentralized market, meaning there’s no central exchange. Instead, trades happen directly between buyers and sellers, typically through online brokers.
The Forex market as we know it today evolved over centuries. Originally, trade between countries was conducted through bartering, but with the growth of international trade, the need for currency exchange became evident.
In the mid-20th century, the Bretton Woods Agreement established fixed exchange rates, which transitioned into a floating system after its collapse in the 1970s. The modern Forex market grew out of these shifts, driven by technological advancements and deregulation, allowing individual traders to participate. Now, the Forex market is the largest financial market in the world, with daily trading volumes surpassing $6 trillion.
Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs in anticipation of price changes. The market price reflects the relative value of one currency against another, influenced by various factors such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events.
For example, when you trade EUR/USD, you are buying euros and selling US dollars simultaneously. Your goal is to profit from the change in the value of the euro relative to the US dollar.
Liquidity and volatility are crucial factors in Forex trading. Here’s why:
Liquidity: The Forex market is highly liquid, meaning currencies can be bought and sold in large volumes without significantly affecting their price. This is important for both large institutional investors and retail traders.
Volatility: Volatility in the Forex market creates opportunities for traders to profit from price swings. Currencies can fluctuate based on economic indicators like interest rates and GDP, or geopolitical events such as elections or trade agreements.
Both liquidity and volatility contribute to the attractiveness of the Forex market but also bring risks that traders must manage effectively.
Impact of Economic Indicators on Forex Market Liquidity and Volatility
| Economic Indicator | Impact on Liquidity | Impact on Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Increases liquidity as markets react quickly to rate changes. | Can cause sharp price movements based on expected rate hikes or cuts. |
| GDP Growth | Generally increases liquidity during periods of stable growth. | Fluctuates significantly based on quarterly reports. |
| Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) | May cause spikes in liquidity when data is released. | Typically increases volatility due to market anticipation and surprises. |
| Inflation | Can affect liquidity if inflation figures change dramatically. | Can drive high volatility in currency pairs like USD/JPY or EUR/USD. |
Understanding Forex currency pairs and key economic indicators is essential for successful trading. In this cluster, we’ll explore how currency pairs work, the role of major economic indicators, and how they influence market movements.
Currency Pairs Explained: Forex currency pairs consist of two currencies, with one being bought and the other sold simultaneously.
Types of Currency Pairs:
Major Pairs: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, etc.
Minor Pairs: Pairs that exclude USD, like EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY.
Exotic Pairs: Includes a major currency and a currency from an emerging market (e.g., USD/TRY).
Base and Quote Currency: The first currency listed is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency (e.g., in EUR/USD, EUR is the base currency).
Bid and Ask Prices: The bid price represents what buyers are willing to pay, and the ask price is the price sellers are willing to accept.
Economic indicators play a pivotal role in determining currency value fluctuations. They are data points that reflect the economic health of a country and significantly influence Forex trading decisions. For instance, interest rates set by central banks can directly affect currency demand. When interest rates rise, currencies tend to appreciate because higher rates attract foreign investment. Other key indicators include the GDP, which reflects the overall economic growth, and retail sales, which indicate consumer confidence and spending power.
On the other hand, indicators like unemployment rate or consumer price index (CPI) can provide insight into inflationary trends, which impact currency stability. Forex traders rely heavily on these indicators to forecast price movements and make informed decisions. Being aware of when important reports are released, such as Non-Farm Payrolls, can give traders an edge by predicting short-term currency movements.

Interest Rates: Set by central banks, interest rates impact currency strength and are crucial for traders to monitor.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The overall economic output of a country, indicating growth or contraction.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): Measures inflation by tracking changes in the price of goods and services.
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP): A critical U.S. indicator that reveals job growth, influencing USD value.
Unemployment Rate: A high unemployment rate can weaken a currency, indicating economic struggle.
| Currency Pair | Average Daily Movement | Impacting Indicators | Suitable for: |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 70-100 pips | Economic growth, ECB decisions | Day Trading, Swing Trading |
| GBP/USD | 80-120 pips | GDP, Inflation, Brexit news | Scalping, Day Trading |
| USD/JPY | 60-80 pips | U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls, BoJ policies | Swing Trading, Position Trading |
| USD/CHF | 50-70 pips | U.S. economic reports, geopolitical events | Swing Trading |
| AUD/USD | 40-60 pips | Commodity prices, Australian GDP | Trend Following, Breakout Trading |
This table illustrates the volatility of popular Forex currency pairs, showing how their average daily movements can vary depending on economic indicators. Traders use this data to determine the best trading strategies based on expected volatility.
Research and Analysis: Stay updated with reports like CPI, GDP, and unemployment rates for economic health insights.
Focus on Timing: Pay attention to when major economic reports, like the Non-Farm Payrolls, are scheduled to release.
Use in Conjunction with Technical Analysis: Combine economic indicators with tools like Moving Averages or Bollinger Bands to enhance predictions.
Monitor Central Bank Announcements: Central bank meetings (like those from the Federal Reserve or European Central Bank) significantly impact currency pairs, especially major ones like EUR/USD.
Mastering the intricacies of Forex currency pairs and understanding economic indicators is critical to improving your trading performance. By monitoring key indicators and analyzing their effects on currency movements, traders can make more informed decisions in the dynamic Forex market. As you progress in your trading journey, these foundational elements will serve as the backbone of your strategy, helping you navigate the complexities of Forex trading with greater confidence and precision.
In this cluster, we’ll explore various Forex trading strategies, which are essential for navigating the Forex market effectively. Understanding and implementing the right strategy can make all the difference between success and failure in Forex trading.
Scalping is a short-term trading strategy that focuses on making small, quick profits throughout the day. It requires a deep understanding of market movements and the ability to make rapid decisions.
Typically involves holding positions for minutes or even seconds.
Focuses on exploiting small price movements.
Highly dependent on technical analysis and indicators like Bollinger Bands and MACD.
Suitable for traders who have a strong understanding of liquidity and volatility.
Day trading is another popular strategy where traders buy and sell within the same trading day, aiming to capitalize on short-term market trends. The strategy relies on both technical and fundamental analysis.
Day traders typically use a combination of economic indicators, like interest rates and GDP reports, and technical tools such as Moving Averages to time their trades. The key to success is managing risk and avoiding overnight exposure to unexpected market changes.
Key indicators for day traders:
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP)
Inflation reports
Interest Rate decisions
Day trading can be highly profitable, but it requires discipline, constant attention, and a well-thought-out plan to mitigate risks.
Swing trading involves capturing price swings in the market over several days to weeks. Traders use technical indicators like the Stochastic Oscillator and Fibonacci Retracement to identify potential entry and exit points.
Swing trading is ideal for those who prefer to hold positions longer than day traders but don’t want the long-term exposure associated with position trading.
Entry and exit points are determined using technical analysis.
Requires patience and an understanding of market cycles.
Traders monitor USD/JPY, EUR/USD, and other major currency pairs.
Position trading is a long-term approach where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years, depending on the market trend. This strategy relies more on fundamental analysis and broader economic factors rather than short-term price fluctuations.
A position trader will consider macroeconomic factors like trade balance, GDP, and consumer price index (CPI) data. The goal is to capture long-term trends in currency pairs such as GBP/USD or USD/CHF.
A focus on economic data and trends.
Requires understanding of interest rate differentials.
Traders often use weekly or monthly charts for analysis.
The trend following strategy involves identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing market trend. Traders use technical indicators like Moving Average and RSI to spot trends and trade accordingly.
| Currency Pair | Trend Indicator | Entry Point | Exit Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 50-day Moving Average | Above 1.1000 | Below 1.1200 |
| GBP/USD | RSI (14) | RSI below 30 | RSI above 70 |
| USD/JPY | MACD | MACD crossover | MACD divergence |
Trend following requires consistent monitoring of long-term price trends.
Emphasis on technical over fundamental analysis.
Successful traders often use trailing stops to lock in profits.
Understanding Forex trading strategies is essential for any trader looking to profit from the global currency market. Whether you're using scalping, day trading, or position trading, each strategy offers unique advantages and challenges. By mastering these techniques and understanding the various indicators like Moving Averages, MACD, and RSI, you’ll be better equipped to make informed trading decisions.
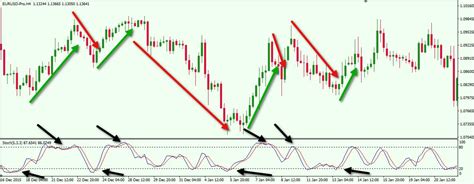
Technical indicators play a vital role in Forex trading as they help traders analyze market trends, price movements, and trading opportunities. Understanding these tools is essential for anyone looking to navigate the Forex market successfully.
Definition: Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on the price, volume, or open interest of a currency pair.
Purpose: They help traders make decisions by identifying trends and patterns.
Common Types: Moving averages, Bollinger Bands, RSI, MACD, etc.
Usage: Used for short-term and long-term analysis, depending on the trading strategy.
Benefits: Provide clarity, enhance decision-making, and can signal entry or exit points.
Moving averages smooth out price data over a specific period, helping traders identify the direction of a trend. The two main types of moving averages used in Forex trading are Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
Comparison Table of SMA and EMA:
| Feature | Simple Moving Average (SMA) | Exponential Moving Average (EMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Calculation Method | Average of past prices | Weighted average of past prices |
| Sensitivity to Price Changes | Less sensitive | More sensitive |
| Common Use | Long-term trends | Short-term trends |
| Popular Periods for Forex Trading | 50, 200 periods | 12, 26 periods |
RSI (Relative Strength Index) and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) are widely used to gauge momentum and identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
RSI:
Measures the speed and change of price movements.
Values range from 0 to 100, with overbought conditions above 70 and oversold conditions below 30.
MACD:
A trend-following momentum indicator.
Consists of two lines: the MACD line and the signal line. When the MACD crosses above the signal line, it’s a buy signal, and vice versa for a sell signal.
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines: the middle line (SMA), the upper band (SMA + 2 standard deviations), and the lower band (SMA - 2 standard deviations).
Market Volatility:
The bands expand and contract based on market volatility.
When the price touches the upper or lower band, it indicates overbought or oversold conditions.
Traders often use the bands to identify breakout opportunities or reversals.
The Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares a currency pair’s closing price to its price range over a set period.
Function:
Measures market momentum and identifies overbought or oversold conditions.
Ranges from 0 to 100, with values above 80 indicating overbought conditions and below 20 indicating oversold.
Usage:
Often used in combination with other indicators to confirm trade signals and improve accuracy.
Introduction:In Forex trading, managing risk and understanding order types are crucial for achieving long-term success. This cluster explores key risk management techniques and various order types used by traders to execute trades effectively.
Importance of Risk Management
Every trader must learn how to manage risk to protect their capital. Without risk management strategies, even skilled traders can experience significant losses.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio
This ratio helps traders decide whether the potential reward justifies the risk. A typical risk-to-reward ratio is 1:2, meaning the potential reward is twice the risk.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when it reaches a pre-set loss limit. This helps minimize losses and protect profits.
Position Sizing
Properly sizing your positions based on account balance and risk tolerance is key to effective risk management. Traders typically risk 1-2% of their capital per trade.
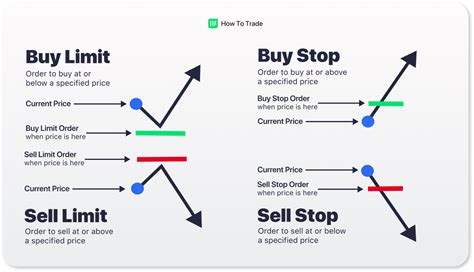
Market Orders
A market order executes immediately at the current market price. It’s the simplest order type used for fast executions.
Limit Orders
A limit order specifies the price at which a trader wants to buy or sell. It is executed when the market reaches the desired price.
Stop Orders
A stop order triggers once a certain price level is reached. Stop orders are commonly used in conjunction with stop-loss strategies to minimize losses.
| Order Type | Description | Execution Speed | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Order | Executes at the current market price | Instant | Best for immediate execution |
| Limit Order | Executes only at a specified price or better | Delayed | Best for entering trades at a specific price |
| Stop Order | Executes once a set price is reached | Delayed (Triggered) | Commonly used for stop-loss or breakout trades |
Using stop-loss orders is one of the most critical elements of risk management in Forex trading. A stop-loss order can help a trader lock in gains and limit losses by automatically closing a position at a specified price. For example, if the EUR/USD pair drops below 1.1500, a stop-loss order would automatically sell your position, preventing further losses. Similarly, take-profit orders automatically close positions when a predetermined profit target is reached, ensuring that traders don't miss out on potential gains due to market reversals.
The strategic use of both stop-loss and take-profit orders helps to keep emotions out of trading decisions and improves consistency in the long run.
Effective risk management and knowledge of order types are essential for navigating the Forex market. Understanding how to set stop-loss and take-profit orders, along with utilizing market, limit, and stop orders, can significantly improve a trader’s ability to control risks and maximize profits.
Mastering Forex trading requires a solid understanding of key concepts, strategies, and tools. By focusing on risk management and familiarizing yourself with different order types, traders can better navigate the complexities of the Forex market and protect their capital. With the right strategies, from controlling risk to utilizing various orders like market and limit orders, Forex traders can develop a disciplined approach that maximizes their potential for long-term success.
Forex trading is the act of buying and selling currency pairs in the global foreign exchange market. It involves trading one currency for another with the aim of making a profit from the price fluctuations.
The most common currency pairs include: - EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) - GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar) - USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
The risk-to-reward ratio helps traders evaluate the potential profit against the possible loss of a trade. A typical ratio is 1:2, where the trader is willing to risk $1 to gain $2. This strategy ensures that losses are kept smaller than profits, providing a better overall risk management strategy.
A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when it reaches a predetermined loss level, helping limit potential losses. For instance, setting a stop-loss order at 50 pips below the entry price will protect your capital by closing the trade if the price moves against you by that amount.
A market order is executed immediately at the current market price, providing fast execution. A limit order, on the other hand, is placed at a specific price and will only execute when the market reaches that level, which could result in a delayed execution.
The **EUR/USD** pair is one of the most traded currency pairs in Forex, representing the Euro against the US Dollar. Its high liquidity and tight spreads make it a popular choice for traders looking for stable and predictable price movements.
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in **Forex trading** by helping traders predict future price movements based on past market data. Tools like **Moving Averages**, **RSI**, and **MACD** assist in identifying trends, momentum, and potential reversal points in the market.
Interest rates are a key factor in **Forex trading** because they influence currency values. When a country raises interest rates, its currency typically strengthens as investors seek higher returns. Conversely, when interest rates are lowered, a currency might weaken due to reduced investment appeal.