
FOREIGN EXCHANGE INTERVENTIONS BY CENTRAL BANKS: MAIN TALKING POINTS
Central banks often deem it necessary to intervene in the foreign exchange market to protect the value of their national currency. Central banks can achieve this by buying or selling foreign exchange reserves or simply by mentioning that a particular currency is under or over-valued, allowing participants of the forex market to do the rest. This article looks at the different types of central bank interventions and important facts to keep in mind before trading.
WHAT IS FOREIGN EXCHANGE INTERVENTION?
Foreign exchange intervention is the process whereby a central bank buys or sells foreign currency in an attempt to stabilize the exchange rate, or to correct misalignments in the forex market. This is often accompanied by a subsequent adjustment, by the central bank, to the money supply to offset any undesirable knock-on effects in the local economy.
The mechanism mentioned above, is referred to as “sterilized intervention” and will be discussed later on, along with the other currency intervention methods.
HOW FOREX TRADERS CAN TRADE A CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION
Traders must keep in mind that when central banks intervene in the forex market, moves can be extremely volatile. Therefore, it is essential to set an appropriate risk to reward ratio and make use of prudent risk management.
Central banks intervene in the forex market when the current trend is in the opposite direction to where the central bank desires the exchange rate to be. Therefore, trading around central bank intervention is a lot like trading reversals.
Additionally, the forex market tends to anticipate central bank intervention meaning that it is not uncommon to see movements against the long-term trend in the moments leading up to central bank intervention. Since there is no guarantee that traders can look for the new trend to emerge before placing a trade.
WHY DO CENTRAL BANKS INTERVENE IN THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET?
Central banks generally agree that intervention is necessary to stimulate the economy or maintain a desired foreign exchange rate. Central banks will often buy foreign currency and sell local currency if the local currency appreciates to a level that renders domestic exports more expensive to foreign nations. Therefore, central banks purposely alter the exchange rate to benefit the local economy.
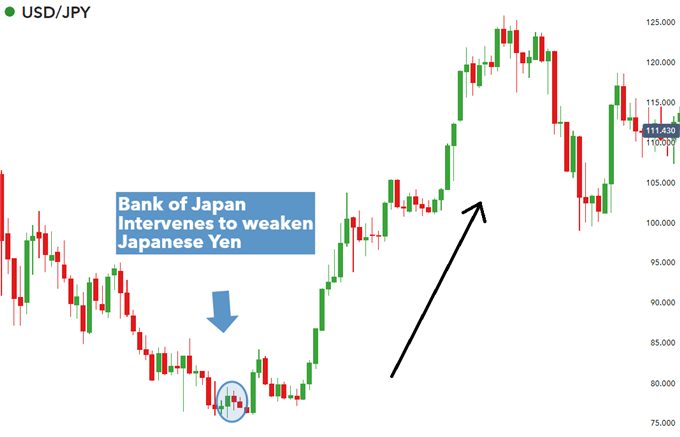
Below is an example of successful central bank intervention in response to Japanese Yen strength against the US dollar. The Bank of Japan was of the view that the exchange rate was unfavorable and swiftly intervened to depreciate the Yen thus, resulting in a move higher for the USD/JPY pair. The intervention took place in the timespan depicted by the blue circle and the effect was realised shortly thereafter.
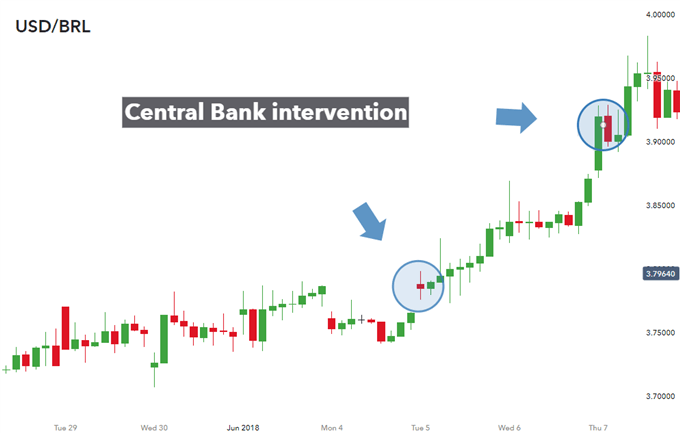
While most central bank intervention is successful, there are instances when this in not the case. The chart below depicts a currency intervention example in the USD/BRL (Brazilian Real) currency pair. The chart highlights both instances where the central bank intervened to stop the decline in the Brazilian Real. It is clear to see that both scenarios failed to immediately strengthen the Real against the US dollar as the dollar continued to rise higher and higher.
Read more on the role of central banks in the forex market.
HOW DOES CURRENCY INTERVENTION WORK?
Central banks have a choice of different types of interventions to make use of. These can either be direct or indirect. Direct intervention, as the name suggests, has an immediate effect on the forex market, while indirect intervention achieves the objectives of the central bank via less invasive means. Below are examples of direct and indirect intervention:
| TYPES OF INTERVENTION | DIRECT OR INDIRECT |
|---|---|
| Jawboning | Indirect |
| Operational Intervention | Direct |
| Concerted Intervention | Direct and indirect |
| Sterilized Intervention | Direct |
Operational Intervention: This is usually what people mean when they refer to central bank intervention. It involves the central bank buying and selling both foreign and local currency to drive the exchange rate to a targeted level. It is the pure size of these transactions that move the market.
Jawboning: this is an example of indirect FX intervention whereby a central bank mentions that it may intervene in the market if the local currency reaches a certain undesirable level. This method, as the name suggests, is more about talking than actual intervention. With the central bank ready to intervene, traders take it upon themselves to collectively bring the currency back to more acceptable levels.
Concerted Intervention: This is a combination of jawboning and operational intervention and is most effective when multiple central banks voice the same concerns over exchange rates. If a number of central banks increase their jawboning efforts, it is likely that one of them actually conducts operational intervention to drive the exchange rate in the desired direction.
Sterilized intervention: Sterilized intervention involves two actions from the central bank in order to influence the exchange rate and at the same time, leave the monetary base unchanged. This involves two steps: The sale or purchase of foreign currency, and an open market operation (selling or buying government securities) of the same size as the first transaction.
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE ROLE OF CENTRAL BANKS AND FOREX TRADING
DailyFX provides a dedicated central bank calendar showing all the scheduled central bank rate announcements for major central banks.
Join Senior Currency Analyst, Christopher Vecchio as he delves into the major central bank trends and data releases via the Central Bank weekly webinar. We have a whole host of webinars covering a wide range of topics and markets. Book your place on the DailyFX webinar calendar.
Keep up to date with crucial central bank announcements or data releases happening this week via our economic calendar.






