In the fast-paced world of Forex trading, the difference between success and failure often comes down to one key factor: analysis. Forex analysis is crucial for traders as it equips them with the insights needed to navigate the volatility and unpredictability of the currency markets. Without a thorough understanding of market trends, economic indicators, and technical signals, traders are left vulnerable to impulsive decisions and unexpected market movements. Whether you rely on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both, mastering these tools is essential to making informed, strategic trades. This article explores why Forex analysis is indispensable and how it can significantly enhance your ability to predict price movements and manage risks effectively.
The Fundamentals of Forex Analysis
Forex analysis is essential for traders seeking to make informed decisions. Understanding economic indicators, central bank actions, geopolitical events, and market sentiment helps traders predict currency pair movements like EURUSD or GBPUSD, driving successful trading strategies.
1.1 Understanding Economic Indicators in Forex Analysis
Inflation Rate: Measures the rate of change in prices of goods and services, impacting currency value. A rising inflation rate often leads to a depreciation in currency value.
GDP Growth: A growing economy typically strengthens a nation's currency. GDP growth signals economic health and increases investor confidence.
Unemployment Rate: A high unemployment rate can indicate economic troubles and negatively impact a currency.
Retail Sales: A key indicator of consumer spending. Higher retail sales often signal economic growth, influencing the demand for a currency.
Manufacturing PMI: Indicates economic health in the manufacturing sector. A strong PMI supports a stronger currency.
By monitoring these indicators, traders can gauge the economic strength of a country and predict future price movements in currency pairs like USDJPY, EURGBP, or AUDUSD.
1.2 The Role of Central Banks in Forex Markets
Central banks play a vital role in shaping the Forex market through monetary policy decisions. For instance, the Federal Reserve or European Central Bank can influence market movements by adjusting interest rates or through quantitative easing. These decisions typically affect currency pairs like USDCHF or EURUSD.
When central banks raise interest rates, it makes a currency more attractive to investors, which tends to drive up the currency's value. On the other hand, lower interest rates often lead to currency depreciation. Furthermore, announcements from central banks regarding inflation targets, economic growth, or monetary policy can have an immediate impact on the Forex market, driving substantial volatility.
Traders who closely follow central bank policies can predict short- and long-term trends in currency prices, making it crucial for informed trading decisions.
1.3 The Impact of Geopolitical Events on Forex
War: Political instability or warfare in key regions can lead to a flight to safety, causing currencies like the USD or CHF to appreciate as investors seek stability.
Trade Agreements: Trade agreements, such as Brexit or US-China trade deals, can significantly influence currency pairs like GBPUSD or USDCAD.
Sanctions: Economic sanctions imposed by one country on another (e.g., US sanctions on Iran) often lead to a decrease in the value of the targeted country's currency.
Elections: Political transitions and election results in countries like the Eurozone or UK can create market uncertainty, impacting currencies like EURGBP or GBPJPY.
Geopolitical events introduce uncertainty, often leading to increased volatility in the Forex market. Traders must be aware of global developments and how they influence currency pairs to manage risk effectively.
1.4 Market Sentiment: A Psychological Analysis
| Market Sentiment | Impact on Currency | Example Indicator/Reaction | Currency Pair Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bullish | Strengthens currency as investors expect positive growth | Rising GDP or consumer confidence data | EURUSD, AUDUSD |
| Bearish | Weakens currency as investors expect negative developments | High unemployment or inflation rates | GBPUSD, USDJPY |
| Neutral | Little to no effect on currency as market waits for direction | Mixed economic data, no clear trend | NZDUSD, EURGBP |
| Risk-On | Investors seek riskier assets, strengthening currencies like AUD | Positive market sentiment, low volatility | AUDJPY, AUDUSD |
| Risk-Off | Investors flock to safe-haven assets like USD or CHF | Geopolitical instability, rising fears | USDCHF, EURUSD |
Market sentiment influences how traders perceive the strength or weakness of a currency. By gauging the market's mood—whether bullish, bearish, or neutral—traders can align their positions with the expected direction of currency pairs.
1.5 Forex Analysis and Economic Cycles
Understanding the economic cycle is vital for Forex traders because it offers insights into long-term trends. Economic cycles, characterized by periods of expansion and contraction, directly affect currency values. During economic expansion, rising GDP, low unemployment, and increasing consumer confidence often lead to stronger currencies. Conversely, during a recession, economic stagnation, rising inflation, and reduced consumer spending can weaken currencies.
For instance, when the Eurozone is in a growth phase, currency pairs like EURUSD might experience upward trends. However, if the region enters a contraction phase, EURUSD may weaken. The ability to predict where a country stands within the economic cycle allows traders to take advantage of shifts in currency values, aligning their trades with broader economic trends.
Technical Tools for Forex Traders
In Forex trading, technical analysis is key for predicting price movements. By utilizing tools such as indicators and chart patterns, traders can make informed decisions based on historical data.
2.1 Popular Technical Indicators and Their Functions
Moving Averages (MA):
Used to smooth out price data and identify the direction of the trend.
Key moving averages include the 50-day, 200-day, and exponential moving averages (EMAs).
Example: EURUSD may show a bullish trend if the price stays above the 200-day MA.
Relative Strength Index (RSI):
Measures the strength and momentum of a currency pair’s price action.
Ranges from 0 to 100, indicating overbought conditions above 70 and oversold below 30.
Example: If USDJPY hits 80, it could be signaling an overbought market.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence):
Helps identify changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend.
The MACD histogram shows the difference between the MACD line and the signal line.
Example: A crossover of the MACD line above the signal line for EURGBP often indicates a potential buy signal.
2.2 Using Fibonacci Retracement in Forex
Fibonacci Retracement is a popular technical tool used to identify potential support and resistance levels by plotting horizontal lines at key Fibonacci levels. These levels include 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%. Traders use these levels to anticipate price pullbacks during trends.
For example, if the GBPUSD currency pair experiences an upward rally and retraces, the Fibonacci levels can help predict where the price might find support before continuing the trend. When the price approaches a 61.8% retracement, it often creates a strong support zone.
Traders typically use these levels alongside other indicators, such as Moving Averages and RSI, to confirm price reversal signals. If both the Fibonacci level and the RSI show oversold conditions, traders may consider entering a long position.
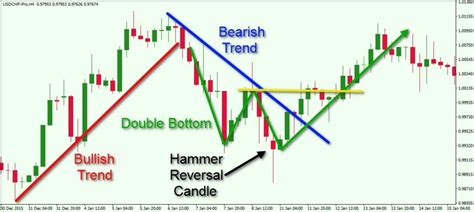
2.3 Candlestick Patterns: A Trader's Guide
| Candlestick Pattern | Description | Trading Signal | Best Used On |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doji | A candlestick with a small body and long shadows. | Indicates market indecision, potential reversal. | EURJPY, GBPUSD |
| Hammer | A small body with a long lower shadow. | A bullish reversal pattern when it appears after a downtrend. | USDCHF, AUDUSD |
| Engulfing | A larger candle completely engulfs the previous one. | Can signal a trend reversal (bullish or bearish). | NZDUSD, EURGBP |
| Shooting Star | A small body with a long upper shadow. | Bearish reversal pattern after an uptrend. | USDJPY, GBPJPY |
2.4 The Role of Volume and Support/Resistance in Price Action
Volume is one of the most important indicators in Forex trading because it indicates the strength behind a price move. Higher volume signifies stronger market interest, while lower volume suggests less conviction. Support and resistance levels are key areas on a price chart where the market has historically reversed or stalled. When a currency pair, such as EURUSD, approaches a major support level during a high-volume trading session, there is a higher probability that the level will hold, causing the price to reverse.
For instance, if USDJPY is trading near a major resistance level with decreasing volume, it may indicate a weakening trend and a potential breakout to the downside. On the other hand, if price breaks through a resistance level with high volume, traders may interpret it as a signal for continued bullish momentum. Thus, volume combined with well-placed support and resistance levels provides a more reliable trading signal.
Mastering technical tools like Moving Averages, RSI, and Fibonacci Retracement is essential for any Forex trader. By understanding how these indicators work and combining them with other tools, traders can predict price movements with greater confidence. Additionally, patterns like candlestick formations and key support/resistance levels, when paired with volume analysis, can further enhance trading decisions. Each of these tools provides critical insight that, when used together, enables traders to create a well-rounded Forex strategy.
Trading Strategies and Forex Analysis

Forex analysis is integral to successful trading strategies. In this cluster, we explore different trading strategies and how Forex analysis helps to shape them, enhancing traders' abilities to make informed decisions in dynamic markets.
3.1 Scalping: Quick Trades and Analysis
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that involves making small, quick profits from minor price movements. To be successful, scalpers rely heavily on real-time analysis and quick decision-making. Here's how Forex analysis aids scalping:
Real-Time Data: Scalpers monitor currency pairs such as EURUSD and GBPUSD with up-to-the-minute charts and data to make rapid decisions.
Technical Indicators: Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average help identify overbought or oversold conditions, signaling the right time to enter or exit trades.
Economic News: Market-moving news such as RetailSales or InterestRate decisions can provide short-term volatility, perfect for scalping opportunities.
Market Liquidity: Scalpers thrive in highly liquid markets. The higher the volume, the more accurate the price movements, especially in major currency pairs like USDJPY and EURJPY.
3.2 Swing Trading and the Role of Technical/Fundamental Analysis
Swing trading typically focuses on capturing gains from medium-term price movements. Traders using this strategy typically hold positions from a few days to weeks, making both technical and fundamental analysis essential.
In technical analysis, swing traders rely on indicators such as MACD, Bollinger Bands, and Support/Resistance levels to identify trend reversals and continuation patterns. These tools help pinpoint optimal entry and exit points, ensuring that trades are made at the peak or trough of a trend.
On the fundamental side, traders will consider economic indicators like GDPGrowth and InflationRate, which influence longer-term price trends. For example, if a central bank such as the European Central Bank hints at future interest rate hikes, traders may expect the EURUSD to appreciate, offering a profitable swing trading opportunity.
Together, these types of analysis give swing traders a balanced view of both the underlying economic factors and the market timing necessary for success.
3.3 Day Trading: Timing Your Entry and Exit
Day trading involves buying and selling currency pairs within the same trading day, relying on precise timing and technical analysis to capture small price fluctuations. Here's how Forex analysis supports this strategy:
<step 1> Identify Market Trends: Use Moving Averages to spot short-term trends and make quick decisions about entry and exit points.
<step 2> Monitor Economic Events: Track news such as UnemploymentRate or ManufacturingPMI releases, as these can drastically influence market sentiment and currency movements within the day.
<step 3> Risk Management: Implementing stop-loss orders and calculating potential rewards based on volatility (e.g., Bollinger Bands) ensures risk is minimized for each trade.
<step 4> Real-Time Charting: Continuously monitor charts for potential reversals, using indicators like Candlestick Patterns and RSI to determine overbought or oversold conditions.
By combining real-time analysis with economic awareness, day traders can time their entries and exits efficiently.
3.4 Position Trading: A Long-Term View of Forex
Position trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold onto positions for weeks, months, or even years, based on fundamental analysis. This strategy requires a deep understanding of economic cycles and central bank policies that influence currency prices over time.
Traders who use position trading must be patient and informed. They analyze macroeconomic factors such as InterestRate decisions by the FederalReserve or the Bank of England, as these events can signal long-term shifts in currency value. For example, a change in the InterestRate can lead to a prolonged upward or downward movement in pairs like GBPUSD or USDCHF, making them prime candidates for position traders.
Another key component is geopolitical events, such as trade agreements or political instability, which can have a lasting impact on currency pairs. By combining long-term fundamental analysis with periodic technical analysis, position traders can manage large moves over extended periods.
3.5 Algorithmic Trading and the Automation of Forex Analysis
Algorithmic trading uses pre-programmed instructions to automate the trading process based on Forex analysis. Algorithms rely on both technical and fundamental analysis to execute trades quickly and accurately, eliminating emotional biases. Here's a breakdown of how it works:
| Component | Details | Entities Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Indicators | Algorithms use MovingAverage, MACD, and RSI to identify patterns and trends automatically. | EURUSD, USDJPY, GBPUSD are often selected for algorithmic strategies due to their liquidity. |
| Fundamental Data | Algorithms process GDPGrowth, InflationRate, and InterestRate to identify economic shifts. | FederalReserve, EuropeanCentralBank, BankOfEngland provide the fundamental drivers behind algorithmic trading. |
| Speed and Efficiency | Automation allows for faster response to market changes, crucial for high-frequency trades. | USDCHF, AUDUSD, NZDUSD are commonly traded in algorithmic strategies for their price consistency and volatility. |
| Risk Management | Algorithms include preset risk controls like stop-loss orders and position sizing. | Market events such as SocialUnrest or NaturalDisaster can be factored in for risk assessment and trade management. |
Explanation: Algorithmic trading is transforming the Forex market by combining technical and fundamental analysis into a streamlined, automated process. Traders can execute orders at lightning speed, leveraging data from currency pairs like EURGBP or USDJPY, making them a popular choice for algorithmic strategies.
Understanding Forex Market Sentiment

Market sentiment in Forex trading refers to the collective emotions and perceptions of market participants. Understanding sentiment, including whether the market is bullish, bearish, or neutral, is crucial for traders looking to navigate currency pairs like EURUSD or GBPUSD.
4.1 Measuring Market Sentiment and Its Impact on Trading
Market sentiment significantly influences Forex trading decisions. Traders often rely on various tools and indicators to gauge the mood of the market. Here's how to measure sentiment:
Sentiment Indicators: Tools such as the Commitment of Traders (COT) report track positions of large institutions, helping to gauge market bias.
Volume Analysis: Increased volume during price moves can confirm the strength of market sentiment.
Currency Indexes: Some traders track US Dollar Index (DXY) or Euro Currency Index (ECI) to understand broader market sentiment.
News Impact: Geopolitical events, such as elections or trade agreements, can drive dramatic shifts in sentiment.
Market sentiment is key to predicting price trends and timing entries or exits, especially when paired with economic indicators like InterestRate and GDPGrowth.
4.2 The Risk-On/Risk-Off Paradigm
The Risk-On/Risk-Off sentiment shift reflects how investors feel about global risk and uncertainty. When markets are Risk-On, investors are more willing to take on risk, pushing up demand for high-yielding currencies like AUDUSD and GBPJPY. Conversely, Risk-Off periods occur during times of financial instability or geopolitical crises, such as war or political instability, which often lead to a flight to safety, favoring USDCHF and EURGBP.
Risk-On: During economic expansions, low InterestRates and strong ConsumerConfidence drive investors to riskier assets. Currency pairs like AUDUSD and NZDUSD typically outperform in this environment.
Risk-Off: In times of uncertainty, such as terrorism or social unrest, investors retreat to safer assets. The USD tends to strengthen, while risk-sensitive currencies weaken.
These sentiment shifts can significantly impact Forex analysis, and understanding them helps traders predict which currencies may strengthen or weaken over short periods.
4.3 Sentiment Analysis in Forex: A Case Study
To better understand sentiment’s influence on Forex, let’s examine how the Brexit referendum in 2016 impacted market sentiment and currency pairs. The uncertainty leading up to the referendum created extreme market volatility and a Risk-Off sentiment, favoring safe-haven currencies like the USD and CHF while the GBP weakened. Below is a breakdown of how sentiment changed pre- and post-Brexit.
| Time Period | Market Sentiment | Key Currency Pair | Impact on Currency | Key Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Brexit (June 2016) | Risk-Off (Uncertainty) | GBPUSD | GBP weakened due to Brexit concerns | Brexit Referendum Announcement |
| Post-Brexit Vote (June 2016) | Bearish (Market Shock) | GBPUSD | GBP plummeted to record lows | Brexit Result (Leave Majority) |
| Post-Referendum (July 2016) | Risk-Off (Flight to Safety) | USDJPY | USD strengthened as investors fled to safe assets | Political Instability and Economic Uncertainty |
This case study clearly illustrates how sentiment analysis can guide traders in understanding how political events or geopolitical risks shift market conditions and affect currency value. Understanding market sentiment during such events allows traders to predict future price actions more effectively.






