The Swiss National Bank (SNB) is Switzerland’s Central bank. Their mission is to promote and maintain monetary and financial stability. It is important for traders to keep up to date with the SNB’s latest changes to monetary policy because it can have a large effect on the Swiss Franc (CHF).

WHAT IS THE SNB?
The Swiss National Bank was established in 1907. It is responsible for the monetary policy of Switzerland and issues Swiss Franc banknotes. As of 2015, the Swiss National Bank is privately owned with most shares belonging to the Swiss Cantons. Like other central banks, the SNB uses different monetary policy tools to bring about price stability and take account of economic developments.
The factor that holds the most importance to traders is monetary policy, which we will explain in depth in this article. Other factors, like the independence of the central bank are also important but are more prevalent issues in emerging market economies.
KEY ECONOMIC MANDATES OF THE SWISS NATIONAL BANK
According to the Swiss National Bank, their primary goals are:
1. Price stability - which is stability of the exchange rate and/or inflation
2. Economic development - which is focus of development and stability of the economy
Price Stability
Monetary policy is extremely important for the entire economy. It prevents runaway inflation and attempts to ground inflation expectations so that the economy can grow at a regular pace. In order to maintain price stability, the Swiss National Bank and their monetary policy committee (MPC) have set an inflation target of less than 2% for CPI per annum.
If inflation goes above the target of 2%, the Swiss National Bank may have to increase interest rates. The increase in interest rates may cause an appreciation in the Swiss Franc (CHF) as investors increase capital flows into the higher yielding currency. It may also have a negative effect on the stock market, as businesses will have to pay higher rates to lend and equity valuations will be discounted at a higher interest rate. Monetary policy data can be found on our economic calendar.
However, it is not always the case that the Swiss National Bank will increase interest rates if inflation is above target. In some cases, like when GDP growth is still low or negative, the Swiss National Bank may keep interest rates low to stimulate the economy. It is important to understand that the Swiss National Bank will be looking for a balance between healthy inflation and economic growth.
Join our central bank webinar to watch our senior currency strategist discuss and analyze current central bank trends.
Economic Development
Economic developments are intertwined with monetary policy. Changes in economic outlook often cause central bankers to update their monetary policy plans in order to stabilize the economy.
HOW SNB INTEREST RATES AFFECT THE SWISS FRANC (CHF)
The Swiss National Bank can affect the value of the Swiss Franc through changes in interest rate expectations. Traders should understand that currencies appreciate/depreciate when interest rate expectations increase/decrease, not just from increases in the nominal interest rate.
The Swiss Central Bank, like most central banks, use different monetary policy tools to control the interest rate. The forex market normally prices in current interest rate expectations, changes in these expectations can cause the Swiss Franc to depreciate or appreciate. The Swiss National Bank can do this by giving the market forward guidance (telling the market) that they expect further hikes or less hikes (or cuts) in the future.
The general principle for how interest rates affects the Swiss Franc and the stock market are given below:
Higher interest rate expectations increase the strength of the Swiss Franc and negatively affect equity values.
Lower interest rate expectations decrease the strength of the Swiss Franc and positively affect equity values.
Interest rate impact on the economy
The Swiss National Bank lowers interest rates when it is trying to stimulate the economy (GDP) and increases interest rates when it is trying to contain inflation caused by an economy operating above potential (overheating).
Lower interest rates stimulate an economy in a few ways:
Businesses can borrow money and invest in projects that will receive more than the risk borrowing rate.
When interest rates are lower the stock market is discounted at a lower rate, leading to an appreciation in stock market values which causes a wealth effect.
People invest their money into the economy (stocks and other assets) because they can earn more in these assets than at currently low interest rates.
How to trade SNB interest rate decisions
The table below displays the possible scenarios that come from a change in interest rate expectations, traders can use this information to forecast if the currency is likely to appreciate or depreciate and how to trade it.
| MARKET EXPECTATIONS | ACTUAL RESULTS | RESULTING FX IMPACT |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Hike | Rate Hold | Depreciation of currency |
| Rate Cut | Rate Hold | Appreciation of currency |
| Rate Hold | Rate Hike | Appreciation of currency |
| Rate Hold | Rate Cut | Depreciation of currency |
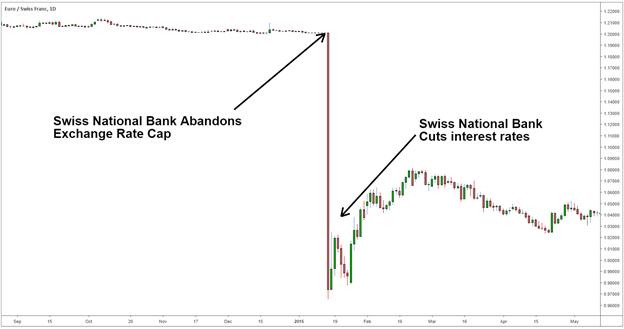
Let’s look at the example below on the EUR/CHF. In 2015 the Swiss National Bank took the market by surprise by abandoning an exchange rate cap on the Swiss Franc. The Swiss Franc, which was capped to the EUR at 1.2 francs per Euro appreciated around 20% initially, policy makers then began to cut interest rates leading to a depreciation of the Swiss Franc.
TOP TAKEAWAYS OF THE SNB AND FOREX TRADING
The Swiss National Bank is fundamental to the value of the Swiss Franc.
The Swiss Franc will appreciate or depreciate depending on changes in interest rate expectations, not on actual changes.
Quantitative easing has a similar effect to changes in interest rates. Changes in expectations of quantitative easing will have an effect on the Swiss Franc.
Rising inflation does not mean the Swiss National Bank will increase interest rates, it depends on the balance between economic growth and inflation.






