The global currency market operates around the clock, creating opportunities for traders in different time zones. The forex market follows a 24-hour cycle, driven by major financial centers such as London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. Understanding when different trading sessions open is essential for identifying periods of high liquidity and volatility. Each session has distinct characteristics, influenced by market participants, economic data releases, and geopolitical events. Traders who align their strategies with the opening and closing times of key financial hubs can improve execution efficiency and capitalize on market movements.
Forex Market Trading Sessions and Opening Hours
The forex market operates continuously across different global financial centers, ensuring seamless trading opportunities. Understanding the distinct characteristics of trading sessions is crucial for aligning strategies with market activity. Liquidity, volatility, and market participants shift throughout the day, influencing price movements.
Global Forex Market Structure
The decentralized nature of the forex market allows for uninterrupted trading across time zones. Unlike stock exchanges, which have fixed opening and closing hours, forex trading follows a cycle dictated by global financial hubs.
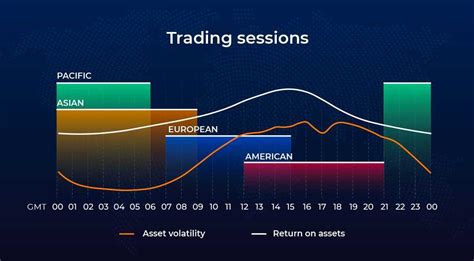
24-Hour Cycle: The forex market moves through key financial centers, creating overlapping sessions that influence liquidity.
Market Participants: Central Banks, Commercial Banks, Hedge Funds, and Retail Traders engage in trading, contributing to price fluctuations.
Liquidity Fluctuations: Currency pairs such as the US Dollar, Euro, and Japanese Yen experience varying liquidity depending on the session.
Economic Data Releases: Indicators like Inflation Rate, Interest Rates, and GDP Growth impact market sentiment.
A clear understanding of this structure enables traders to capitalize on optimal trading hours.
Major Forex Trading Sessions: Asian, European, and North American
Forex trading is divided into three primary sessions, each exhibiting unique characteristics based on economic activity and liquidity flows.
| Session | Primary Financial Hubs | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Asian Session | Tokyo, Sydney | Lower volatility, key movements in JPY, AUD, NZD pairs. |
| European Session | London, Frankfurt | Highest liquidity, significant price movements in EUR, GBP, CHF. |
| North American Session | New York, Toronto | Overlaps with London, major movements in USD pairs. |
Asian Session: Lower trading volumes with occasional sharp moves due to early market reactions.
European Session: Considered the most liquid session, featuring major trading pairs with the British Pound and Euro.
North American Session: New York traders react to European price action, often driving major trends.
Each session contributes to daily price action, making timing an essential element in strategy development.
Sydney and Tokyo Session Dynamics
Currency movements during the Sydney and Tokyo sessions set the tone for the trading day, particularly for currency pairs involving the Australian Dollar, Japanese Yen, and New Zealand Dollar.
Sydney Market Open
The first major trading session of the day.
Often exhibits lower volatility, with price action influenced by carry trade flows.
Impacts AUD/USD, NZD/USD, and USD/JPY movements.
Tokyo Market Influence
Japanese institutional investors, including the Bank of Japan, influence market sentiment.
Traders monitor economic indicators such as Retail Sales, Trade Balance, and Manufacturing PMI.
Liquidity remains moderate, increasing as London markets prepare to open.
Key Trading Considerations
Scalping and Swing Trading strategies work best in these sessions due to lower volatility.
Pairs such as EUR/JPY and GBP/JPY experience higher-than-usual movement due to cross-currency flows.
The performance of Asian stock indices like the Nikkei 225 can influence forex price action.
Monitoring this session helps traders anticipate momentum leading into the European market open.
London and New York Overlap: The Most Volatile Period
The highest liquidity occurs when the London and New York sessions overlap, typically between 12:00 PM and 4:00 PM GMT.
Institutional Trading Surge:
Central Banks, Investment Managers, and Brokers actively trade during this time.
Hedge funds deploy Day Trading and Breakout Trading strategies to capitalize on volatility.
Key Currency Movements:
The US Dollar, Euro, and British Pound experience the highest trading volumes.
High-impact economic releases from the Federal Reserve and European Central Bank drive price fluctuations.
Volatility Peaks:
Traders often observe Moving Averages, MACD, and Support Levels for breakout signals.
Stop-loss orders trigger rapid price movements, creating opportunities for momentum-based trading.
Engaging in trading during this overlap period provides the best conditions for capturing short-term price movements.
Weekend Gaps and Market Open on Monday
Forex trading pauses over the weekend, yet price action resumes with significant movements when markets reopen on Monday morning.
What Causes Weekend Gaps?
Geopolitical Events: Unexpected news can cause price gaps in the US Dollar and Japanese Yen.
Market Close Positions: Hedge funds and Retail Traders adjust positions before the weekend.
How to Trade Weekend Gaps
Traders use Limit Orders and Stop Loss Orders to manage risk.
Breakout Trading is effective when price gaps lead to new trends.
Monday Market Open Considerations
Sydney and Tokyo sessions dictate the early market sentiment.
Carry Trade Unwinding can cause rapid movements in AUD/JPY and NZD/JPY pairs.
Being aware of these dynamics helps traders adjust risk exposure and execute strategic trades at market open.
How Market Participants Influence the Forex Market
Market participants shape forex price movements through liquidity, trading volume, and sentiment shifts. Central Banks, Hedge Funds, Retail Traders, and Corporations play distinct roles in currency valuation. Their activities, from monetary policy decisions to hedging strategies, influence price fluctuations and trading opportunities.
Central Banks and Monetary Policy Impact
Central Banks hold significant influence over currency valuations through policy decisions and direct market interventions.
Interest Rate Decisions
Central Banks adjust Interest Rates to control inflation and economic growth.
Higher rates attract foreign investment, strengthening a currency.
Quantitative Easing and Liquidity Control
Asset purchases or sales impact money supply, affecting Inflation Rate and currency demand.
Expansionary policies weaken a currency, while contractionary measures strengthen it.
Market Interventions
Direct buying/selling of a currency stabilizes excessive fluctuations.
Example: The Swiss National Bank’s intervention to cap the Swiss Franc’s appreciation.
Central Bank policies create long-term trends in the forex market, influencing trading strategies.

Hedge Funds and Speculators Driving Volatility
Hedge Funds and Speculators use large capital reserves to drive price momentum, amplifying market fluctuations.
| Participant Type | Trading Influence | Common Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Hedge Funds | Execute high-volume trades, moving major currency pairs | Trend Following, Carry Trade, Breakout Trading |
| Speculators | Take short-term positions based on price action and news | Day Trading, Scalping, News Trading |
| Dealers | Provide liquidity, setting bid-ask spreads | Market Making, Risk Hedging |
Momentum Creation: Hedge funds deploy large-volume trades that set off chain reactions in currency trends.
News and Speculation: Key economic releases such as GDP Growth and Consumer Confidence lead to speculative trading.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Algorithmic traders execute thousands of trades per second, exploiting price inefficiencies.
Institutional trading accounts for a significant portion of daily forex market turnover, increasing volatility.
The Role of Retail Traders in Market Sentiment
Retail traders form a growing portion of the forex market, contributing to price movements through sentiment-driven trading.
Trading Styles and Their Market Impact
Scalping: Frequent short-term trades affect micro price fluctuations.
Swing Trading: Medium-term trades capture larger market trends.
Position Trading: Long-term strategies align with fundamental analysis.
Retail Trader Sentiment
Online platforms provide sentiment analysis based on retail positioning.
Extreme sentiment levels often lead to trend reversals.
Leverage and Market Exposure
Margin trading allows small investors to control large positions.
High leverage can amplify price swings, especially in volatile currency pairs like GBP/USD and USD/JPY.
Retail traders influence intraday volatility, reacting quickly to news events and market speculation.
Corporations and Trade Balance Considerations
Corporations engage in forex trading to manage currency risk, influencing exchange rates through hedging strategies.
Importers and Exporters
Trade Balance affects currency demand; surplus strengthens a currency, while a deficit weakens it.
Corporations hedge transactions to lock in favorable rates.
Multinational Companies and Currency Exposure
Large firms hedge earnings against currency fluctuations using Forward Contracts and Options.
Example: Apple Inc. hedging against US Dollar volatility.
Foreign Direct Investments (FDI)
Capital inflows impact exchange rates, particularly in emerging markets.
Investors monitor GDP Growth, Inflation Rate, and Consumer Confidence for macroeconomic trends.
Corporate forex activities influence long-term price stability and trading liquidity.
Economic Indicators and Their Effect on Forex Market Movements
Economic indicators provide critical insights into currency movements, influencing trading strategies and risk management. Interest Rates, GDP Growth, Inflation Rate, and Trade Balance play a vital role in determining currency strength. Traders use these data points to anticipate market trends and adjust their positions accordingly.
Interest Rate Decisions and Their Market Influence
Central Banks adjust Interest Rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth, directly affecting forex market liquidity.
Rising Interest Rates
Attract foreign investment, increasing demand for a currency.
Strengthen currencies such as the US Dollar, Euro, and British Pound when rates increase.
Lowering Interest Rates
Reduces returns on investments, leading to capital outflows.
Weakens a currency, making it less attractive for carry trades.
Impact on Trading Strategies
Carry Trading benefits from rate differentials between strong and weak currencies.
Trend Following traders monitor rate hikes for long-term positioning.
Central Banks, including the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of Japan, influence forex trends through monetary policies.
GDP Growth and Its Relationship with Currency Value
A country’s economic output directly correlates with its currency’s strength. Higher GDP Growth signals economic stability, increasing demand for the national currency.
| Currency | GDP Growth Impact | Forex Market Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| US Dollar | Strong GDP data boosts investor confidence | USD appreciates against weaker economies |
| Euro | Growth disparities between EU nations affect overall strength | EUR fluctuates based on economic reports |
| Japanese Yen | Low GDP growth often leads to Bank of Japan interventions | JPY depreciates with negative economic reports |
| British Pound | Higher GDP supports rate hikes by the Bank of England | GBP strengthens in a growing economy |
Trading Implications
Positive GDP Growth encourages foreign investment, strengthening currency demand.
Weak GDP data signals potential monetary easing, leading to depreciation.
Traders analyze GDP figures to forecast market sentiment and position their trades accordingly.
Inflation Rates and Forex Volatility
Changes in Inflation Rates influence Interest Rate Decisions, impacting forex volatility.
High Inflation
Weakens a currency by eroding purchasing power.
Triggers Central Bank interventions to stabilize price levels.
Low Inflation
Encourages economic expansion and long-term currency appreciation.
Keeps Interest Rates steady, reducing speculation-driven price swings.
Trading Relevance
Inflation reports guide traders in adjusting Stop Loss Orders and risk exposure.
Breakout Trading strategies capitalize on price surges following inflation news releases.
Economic indicators such as Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) provide insights into inflation trends.
Employment Data and the Forex Market
Labor market conditions shape monetary policy, influencing currency valuation.
Unemployment Rate Impact
A falling Unemployment Rate signals economic growth, strengthening the national currency.
Rising unemployment may prompt interest rate cuts, weakening currency demand.
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) Reports
Released monthly by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
High NFP figures drive demand for US Dollar, while weak data leads to depreciation.
Job Growth Trends and Forex Trading
Strong employment numbers support trend continuation in currency pairs such as USD/JPY and EUR/USD.
Sudden labor market shifts create volatility, impacting Scalping and Day Trading strategies.
Employment data influences Central Bank policies, making it a key driver of forex movements.
Trade Balance and Its Effect on Exchange Rates
The Trade Balance reflects the difference between a country's exports and imports, affecting currency demand.
Trade Surplus
Occurs when exports exceed imports, increasing demand for the domestic currency.
Countries like China and Germany often experience currency appreciation due to trade surpluses.
Trade Deficit
Imports exceeding exports weaken currency demand.
The US Dollar often fluctuates based on its trade relationships with key partners.
Forex Trading Implications
Traders monitor Export-Import Data to assess long-term trends.
Range Trading strategies capitalize on currency fluctuations driven by trade imbalances.
Monitoring trade reports helps traders identify macroeconomic trends affecting currency valuations.
Consumer Confidence and Market Sentiment
Consumer sentiment influences spending patterns, affecting Retail Sales and economic expansion. High Consumer Confidence correlates with currency appreciation.
How Confidence Affects Forex Movements
Rising confidence boosts household spending, strengthening economic indicators.
Declining confidence weakens the national currency, prompting risk-averse trading behavior.
Key Indicators to Watch
Consumer Confidence Index (CCI)
University of Michigan Sentiment Index
Market Reactions
Positive sentiment encourages bullish positions in major currency pairs.
A drop in confidence triggers safe-haven buying, benefiting Japanese Yen and Swiss Franc.
Consumer sentiment serves as an early indicator of economic health, influencing forex strategies.
Trading Strategies Aligned with Market Openings
Market openings create trading opportunities as liquidity surges and volatility increases. Traders utilize Day Trading, Swing Trading, and Breakout Trading to capitalize on price movements. Understanding session-specific dynamics enhances trade execution and risk management.

Day Trading Strategies for High-Volatility Sessions
Day traders rely on short-term price fluctuations, especially during major session overlaps.
London and New York Overlap
The most liquid trading hours with rapid price movements.
Pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY see significant volatility.
Scalping vs. Momentum Trading
Scalping focuses on small profits from frequent trades.
Momentum Trading aims for breakouts triggered by news events.
Risk Considerations
Stop Loss Orders limit downside risk in volatile conditions.
Leverage enhances gains but increases exposure to rapid reversals.
Day traders benefit from real-time technical indicators such as Moving Averages, MACD, and Bollinger Bands to refine their strategies.
Swing Trading Across Different Trading Sessions
Swing traders hold positions for multiple days, taking advantage of trends across market sessions.
| Trading Factor | Impact on Swing Trading | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Session Timing | Trends form over multiple trading sessions | Traders align entries with market momentum |
| Economic Events | Major news impacts medium-term trends | GDP Growth, Interest Rates, and Inflation Rate affect trades |
| Technical Indicators | Used to confirm trend direction | Fibonacci Retracement, Support Levels, and Ichimoku Cloud guide entries |
Best Pairs for Swing Trading
GBP/JPY and EUR/USD exhibit strong multi-day trends.
Commodity currencies like AUD/USD and NZD/USD react to macroeconomic shifts.
Trade Execution Approach
Enter trades after session transitions to confirm direction.
Use Trailing Stop Orders to lock in profits during extended moves.
Swing trading strategies benefit from aligning trade entries with macroeconomic cycles.
Breakout Trading Strategies for Session Openings
Breakout trading focuses on price movements at session openings, where liquidity spikes lead to significant momentum shifts.
Key Session Breakout Opportunities
The Asian Session Open often sets the day’s initial trading range.
London Open triggers the highest volatility due to European market liquidity.
New York Open adds further volume, leading to decisive price breakouts.
Indicators for Breakout Trading
Bollinger Bands signal volatility expansion.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) confirms momentum strength.
Support and Resistance Levels help define breakout zones.
Trade Setup for Breakout Strategies
Identify consolidation patterns before a session opens.
Enter positions when price breaches significant support or resistance levels.
Use Take Profit Orders to capture early session movements.
Breakout trading is most effective when combined with strong fundamental drivers like economic releases and monetary policy decisions.
Risk Management and Order Types for Session-Specific Trading
Market conditions change across trading sessions, requiring traders to adjust their risk management and order execution strategies. Leverage, Volatility, Currency Correlations, and Order Types influence profitability and risk exposure. Adapting to session-specific characteristics ensures more precise trade execution.
The Role of Leverage and Margin in Different Trading Sessions
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with smaller capital, but it also magnifies risk. Different trading sessions impact margin requirements and leverage efficiency.
London Session:
High liquidity supports moderate leverage strategies.
Lower spreads reduce costs for Scalping and Day Trading.
New York Session:
Overlap with London increases short-term price fluctuations.
Traders use Risk-Reward Ratios to balance leverage exposure.
Asian Session:
Lower volatility allows for Position Trading with reduced margin requirements.
Carry Trades become more attractive due to interest rate differentials.
Traders must align leverage usage with session volatility to minimize unnecessary risk exposure.
Volatility Considerations and Stop Loss Placement
Market volatility varies across sessions, requiring strategic Stop Loss Order placement.
High-Volatility Sessions (London and New York Overlap)
Stop loss levels must account for whipsaw price action.
Wider stops help avoid premature trade exits.
Moderate-Volatility Sessions (Asian and Early London)
Tighter stops reduce exposure in range-bound trading.
Bollinger Bands and Ichimoku Cloud assist in defining risk levels.
Event-Driven Volatility (News Trading)
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP), Interest Rate Decisions, and Inflation Reports cause rapid price swings.
Trailing Stop Orders help lock in profits while managing risk.
Stop loss placement should adjust to session-specific volatility, reducing exposure to erratic price movements.
Correlation Between Currencies and Session-Specific Trading
Currency pairs react differently across market sessions, influencing trade selection.
| Currency Pair | Best Session for Trading | Correlation Insights |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | London & New York | High liquidity and trend-driven movements. |
| USD/JPY | New York & Asian | Reacts to US economic releases and Japanese monetary policy. |
| GBP/JPY | London | Volatile pair influenced by UK economic indicators. |
| AUD/USD | Asian | Correlates with commodity prices and trade balance data. |
London Session Pairs: GBP/USD, EUR/USD, and EUR/GBP show increased activity due to European economic data.
New York Session Pairs: USD/CAD and USD/JPY react to US market sentiment and oil price fluctuations.
Asian Session Pairs: AUD/JPY and NZD/USD exhibit stable price movements tied to trade balance and interest rates.
Traders who align strategies with currency-specific session movements enhance trade precision and profitability.
Order Types and Execution Strategies for Different Market Hours
Market conditions determine the effectiveness of various Order Types during specific trading sessions.
Market Orders:
Useful in high-liquidity periods like the London and New York overlap.
Faster execution but susceptible to slippage in volatile conditions.
Limit Orders:
Ideal for low-volatility sessions where precise entry levels matter.
Helps avoid spreads widening in early Asian market hours.
Stop Loss Orders:
Essential in high-impact news events to manage risk.
Adaptive Trailing Stops secure profits in extended trends.
Take Profit Orders:
Used in Swing Trading across different sessions.
Ensures gains are locked in before market reversals.
Choosing the right Order Type for session conditions optimizes trade execution and reduces unnecessary risk.
Conclusion
Understanding when the forex market opens allows traders to navigate the global currency landscape more effectively. Market liquidity and price movements are heavily influenced by trading sessions in major financial hubs, including London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. Each session brings unique opportunities shaped by key market participants such as central banks, hedge funds, and retail traders. Economic data releases, including interest rates, GDP growth, and inflation rate reports, play a significant role in market volatility, affecting how traders execute their strategies.
Aligning trading strategies with market timing can help traders optimize entries and exits, particularly during periods of high volatility such as the London-New York overlap. Effective risk management techniques, including position sizing, stop loss orders, and hedging, are crucial for long-term success in this 24-hour trading environment. Recognizing the interconnection between trading sessions, economic indicators, and strategic execution ensures traders can make informed decisions and maximize opportunities in the dynamic world of foreign exchange.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, opening in Sydney at 10 PM GMT on Sunday and closing in New York at 10 PM GMT on Friday. The main sessions follow this sequence:
Sydney: 10 PM GMT – 7 AM GMT
Tokyo: 12 AM GMT – 9 AM GMT
London: 8 AM GMT – 5 PM GMT
New York: 1 PM GMT – 10 PM GMT
Central banks play a crucial role in currency valuation through monetary policies and interventions. Interest rate changes, foreign exchange reserves adjustments, and quantitative easing measures all impact currency strength. Traders closely monitor central bank decisions, particularly from the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of Japan, as their policies shape the broader market environment.
The London session is the most active due to:
High liquidity, making it easier to execute trades with minimal slippage.
Significant overlap with the New York session, increasing volatility.
The presence of major financial institutions, hedge funds, and corporate traders.
Several economic indicators influence currency movements, including:
Interest rates: Higher rates strengthen a currency, while lower rates weaken it.
GDP growth: A strong economy attracts investors, boosting currency value.
Inflation rate: Rising inflation can lead to interest rate hikes, affecting forex trends.
Unemployment rate: Lower jobless rates often signal economic strength.
During session overlaps, traders often use:
Breakout trading: Capturing price surges when liquidity increases.
Scalping: Quick trades on small price movements in volatile conditions.
Swing trading: Taking advantage of longer-term trends forming in high-volume hours.
Effective risk management in the forex market includes:
Setting appropriate stop loss orders to limit potential losses.
Using position sizing to ensure capital is not overexposed.
Hedging currency positions to offset potential risks.
Monitoring market volatility and adjusting strategies accordingly.






